Mulching is a common practice in outdoor gardening, but it can also be highly beneficial for indoor plants. Mulch helps regulate moisture, improve soil health, and enhance the aesthetic appeal of your potted plants. In this guide, we’ll explore how to use mulch effectively for your indoor plants.
What is Mulch?
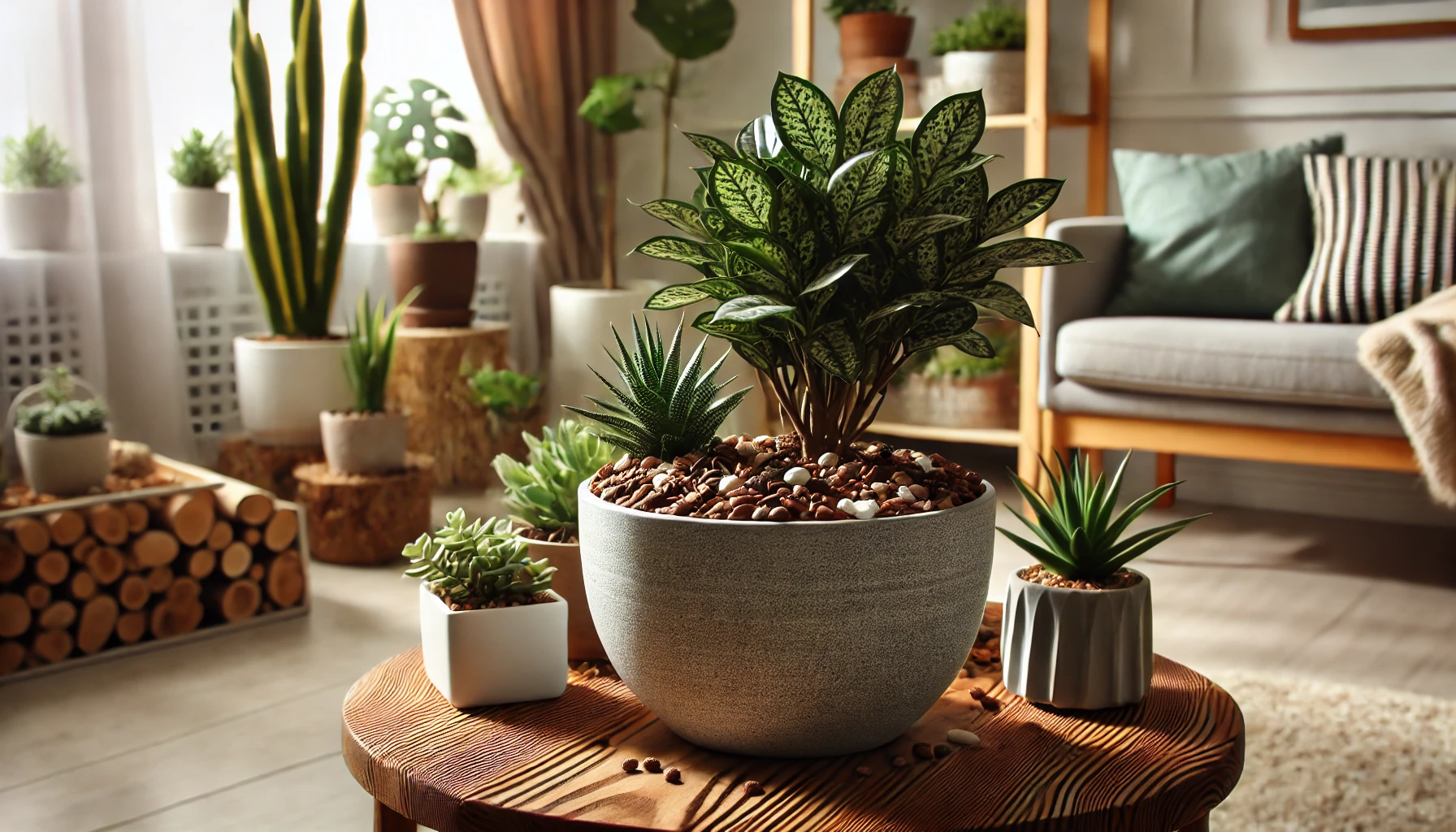
Mulch is a layer of organic or inorganic material applied to the soil’s surface. It serves multiple purposes, such as retaining moisture, preventing weeds, and insulating roots. For indoor plants, mulch is used primarily for moisture control and decorative purposes.
Benefits of Mulch for Indoor Plants
1. Moisture Retention
- Mulch reduces water evaporation, keeping the soil moist for longer periods.
- This is especially helpful for plants that require consistent hydration, such as tropical varieties.
2. Temperature Regulation
- Mulch insulates the soil, protecting roots from temperature fluctuations caused by indoor heating or air conditioning.
3. Prevents Soil Erosion
- Mulch stabilizes the soil, reducing the risk of compaction or displacement during watering.
4. Aesthetic Appeal
- Decorative mulch materials like pebbles or bark add a polished look to your indoor plants.
5. Weed Suppression
- While weeds are uncommon indoors, mulch can prevent unwanted growth in larger indoor gardens or planters.
Types of Mulch for Indoor Plants
1. Organic Mulch
- Examples: Bark chips, shredded leaves, coco coir, or compost.
- Benefits: Improves soil health as it decomposes, adding nutrients to the soil.
- Best For: Plants with high nutrient needs, like flowering or fast-growing species.
2. Inorganic Mulch
- Examples: Pebbles, stones, decorative gravel, or glass beads.
- Benefits: Long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing; does not decompose or attract pests.
- Best For: Succulents, cacti, and low-maintenance plants.
How to Apply Mulch to Indoor Plants
Step 1: Prepare the Soil
- Ensure the soil is healthy and free from debris before adding mulch.
- Water the plant thoroughly, as mulch will reduce evaporation.
Step 2: Choose the Right Mulch
- Select a mulch type based on the plant’s needs and your aesthetic preferences.
Step 3: Apply the Mulch
- Spread a thin, even layer (1–2 inches) of mulch over the soil surface.
- Avoid piling mulch against the plant’s stem to prevent rot.
Step 4: Maintain the Mulch
- Check regularly for signs of mold or compaction.
- Refresh organic mulch as it decomposes to maintain its benefits.
Best Practices for Using Mulch Indoors
- Avoid Over-Mulching: Too much mulch can trap excess moisture and lead to root rot.
- Monitor for Pests: Organic mulch may attract pests if not maintained properly.
- Match Aesthetics: Choose mulch that complements your plant and pot for a cohesive look.
- Pair with Proper Watering: Mulch helps retain moisture but doesn’t replace the need for a consistent watering routine.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using Outdoor Mulch Indoors: Outdoor mulch may carry pests or pathogens harmful to indoor plants.
- Neglecting to Refresh Mulch: Organic mulch needs to be replaced periodically to maintain its effectiveness.
- Using Non-Breathable Materials: Avoid using materials that block air circulation, as this can suffocate the roots.
Conclusion: Enhance Your Indoor Plant Care with Mulch
Mulching is a simple yet effective way to improve the health and appearance of your indoor plants. By choosing the right type of mulch and applying it properly, you can create a more stable and beautiful environment for your greenery to thrive.