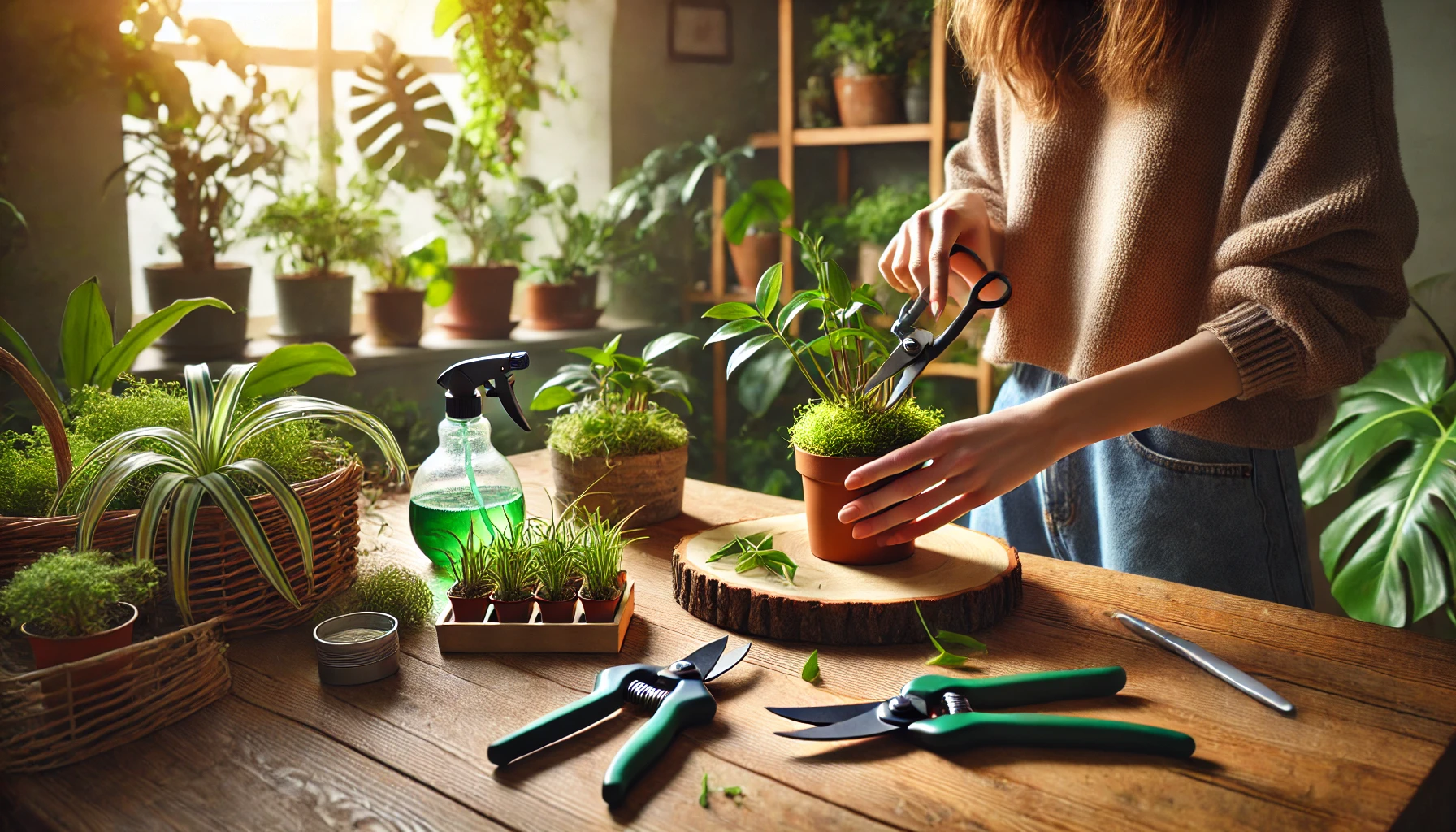
Pruning is an essential practice that helps maintain your plants’ health, encourages new growth, and enhances their overall appearance. When done correctly, pruning can revitalize your plants and prevent common issues such as overcrowding or disease. This guide will show you how to prune your plants effectively.
Why Prune Your Plants?
Pruning offers several benefits, including:
- Promoting Growth: Removes dead or damaged parts, directing energy toward healthy growth.
- Shaping Plants: Maintains a tidy appearance and prevents overgrowth.
- Encouraging Blooms: For flowering plants, pruning can stimulate more vibrant blooms.
- Preventing Disease: Eliminates infected parts before they spread to healthy areas.
Tools You’ll Need
Before you begin, gather these essential tools:
- Pruning Shears: For precise cuts on small to medium stems.
- Scissors: Useful for light trimming of delicate plants.
- Loppers: For thicker branches on larger plants.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from thorns and sap.
- Disinfectant: Clean tools before and after use to prevent the spread of disease.
When to Prune
General Guidelines
- Growing Season: Prune most plants in spring or early summer when they are actively growing.
- Dormant Season: For trees or larger shrubs, prune during late winter when they are dormant.
Signs a Plant Needs Pruning
- Dead or yellowing leaves.
- Overcrowded branches.
- Stunted growth or fewer blooms.
- Diseased or damaged areas.
How to Prune Your Plants
Step 1: Inspect the Plant
Examine the plant to identify:
- Dead or damaged leaves and stems.
- Overgrown or crossing branches.
- Areas with pests or disease.
Step 2: Start with Dead or Diseased Parts
- Remove all yellow, brown, or wilted leaves.
- Cut back any stems showing signs of rot or pests.
Step 3: Shape the Plant
- Trim overgrown stems to create a balanced shape.
- For trailing plants, cut back excessively long vines to encourage fuller growth.
Step 4: Encourage Air Circulation
- Remove overcrowded or crossing branches to improve airflow and light penetration.
Step 5: Prune Above a Node
- Make cuts just above a leaf node or bud to encourage new growth.
- Use clean, angled cuts to prevent water from pooling on the cut surface.
Pruning Tips for Specific Plants
1. Flowering Plants
- Deadhead spent blooms regularly to encourage more flowers.
- Prune heavily after the flowering season to shape the plant.
2. Trailing and Vining Plants
- Trim long, straggly vines to maintain shape and fullness.
- Remove older, woody stems to rejuvenate the plant.
3. Succulents
- Prune leggy growth to maintain a compact shape.
- Allow cut areas to callous before watering to prevent rot.
4. Tropical Plants
- Remove yellow or brown leaves promptly.
- Avoid heavy pruning unless the plant is overgrown.
Common Pruning Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-Pruning: Cutting too much can stress the plant. Stick to removing no more than 20–30% of the plant at a time.
- Using Dirty Tools: Always sterilize tools to prevent spreading diseases.
- Pruning at the Wrong Time: Avoid pruning during dormancy unless necessary for maintenance.
Aftercare Tips
- Watering: Give the plant a light watering after pruning to help it recover.
- Fertilizing: Wait at least a week after pruning before fertilizing to avoid overloading the plant.
- Monitoring: Watch for signs of stress, such as drooping or discoloration, and adjust care as needed.
Conclusion: Pruning for Plant Health and Beauty
Regular pruning is key to maintaining healthy, vibrant plants. By following these tips and techniques, you can ensure your plants grow stronger and more beautiful with each cut. Remember, pruning is not just about removing; it’s about shaping a thriving, flourishing plant.