Replanting, or repotting, is an essential part of plant care that allows your plants to grow healthier and thrive. However, the process can stress plants if not done correctly. This guide will walk you through how to replant your plants safely and effectively, minimizing stress and promoting growth.
When Should You Replant a Plant?
Knowing when to replant is the first step to successful repotting. Look for these signs:
- Roots Are Overcrowded: Visible roots circling inside the pot or growing out of drainage holes.
- Growth Has Slowed: The plant seems stunted despite proper care.
- Soil Drains Poorly: Old soil that retains too much water or lacks nutrients.
- Top-Heavy Plants: The plant tips over easily because it has outgrown its pot.
Choosing the Right Pot and Soil
Pot Selection
- Size: Choose a pot 1–2 inches larger in diameter than the current one. Oversized pots retain excess water, leading to root rot.
- Material: Terracotta pots are breathable and good for most plants, while plastic pots retain moisture better.
Soil Preparation
- Use a soil mix suited to your plant type:
- Cacti and Succulents: Fast-draining, sandy soil.
- Tropical Plants: Rich, organic soil with good moisture retention.
- Orchids: Special orchid mix for proper aeration.
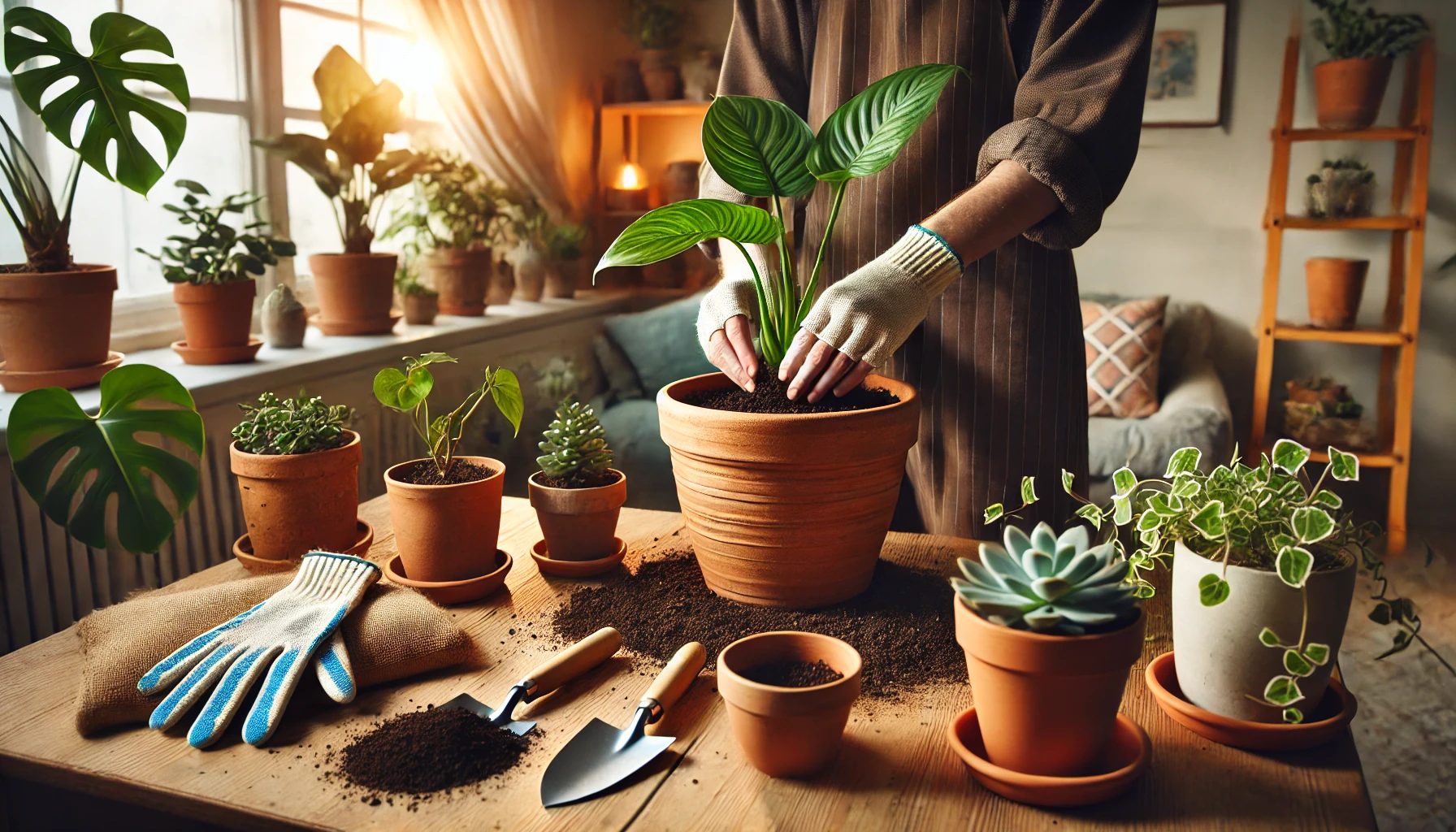
Steps to Replant Your Plant
1. Prepare Your Materials
Gather the new pot, fresh soil, gloves, and any tools you may need, such as a small trowel or scissors.
2. Water Before Replanting
Water the plant a day before replanting. This softens the soil, making it easier to remove the plant without damaging roots.
3. Remove the Plant from Its Pot
- Hold the base of the plant gently and tilt the pot.
- Tap the sides of the pot to loosen the soil and roots.
- For stubborn plants, use a clean knife to run along the pot’s edges.
4. Examine the Roots
- Trim dead or rotting roots with sterilized scissors.
- Untangle any circling roots to encourage outward growth.
5. Add Soil to the New Pot
- Place a layer of fresh soil at the bottom of the new pot.
- Position the plant in the center, ensuring it sits at the same depth as in the previous pot.
6. Fill with Soil
- Add soil around the roots, gently pressing to remove air pockets.
- Avoid packing the soil too tightly to allow proper aeration.
7. Water Thoroughly
After replanting, water the plant thoroughly until water drains from the bottom. This helps settle the soil and hydrate the roots.
Post-Replanting Care
Minimize Stress:
- Place the plant in a shady or low-light area for a few days to recover.
- Avoid fertilizing immediately after repotting, as it can stress the plant further.
Monitor Your Plant:
- Check for signs of stress, such as drooping leaves. This is normal but should improve within a week.
- Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Replanting Too Frequently
Repotting too often can stress plants unnecessarily. Most plants only need repotting every 1–2 years. - Using the Wrong Pot Size
A pot that is too large retains excess water, while one that’s too small restricts root growth. - Skipping Root Inspection
Failing to check roots for rot or damage can lead to ongoing health issues.
Conclusion: A Fresh Start for Your Plants
Replanting is a vital step in keeping your plants healthy and thriving. With careful preparation and proper techniques, you can ensure a smooth transition for your plants, minimizing stress and setting them up for success. By paying attention to their needs and following this guide, your plants will continue to grow and flourish.